Air compressors play a vital role in almost every modern industry. They supply the compressed air that powers pneumatic tools. They support automation and keep production systems running efficiently. In today’s industrial setups, two technologies dominate. These are the reciprocating air compressor and the rotary screw air compressor.
Both systems deliver compressed air, but they work in very different ways. Because of this, the difference affects performance. It also impacts energy efficiency and long-term reliability across the entire facility.
Types of Air Compressors: Reciprocating vs Rotary Screw
Air compressors operate using two main technologies. Each one works differently. These differences help you choose the right system for your compressed air systems.
| Feature / Category | Reciprocating Air Compressor | Rotary Screw Air Compressor |
|---|---|---|
| How It Works | Uses pistons driven by a crankshaft to compress the air. | Uses two meshing helical screws (two screws) to compress the air. |
| Key Components | Piston, cylinder, piston rings, valves, crankshaft. | Internal rotors, inlet filter, oil separator (or oil free design). |
| Airflow Pattern | Delivers high pressure air in short bursts. | Provides steady flow and consistent airflow for long periods. |
| Operation Style | Designed for intermittent use; requires cooling breaks. | Built for continuous operation; supports a true 100% duty cycle. |
| Output Volume | Lower airflow volume; ideal for single-tool tasks. | Large volume output; ideal for multi-equipment industrial systems. |
| Energy Efficiency | Less efficient due to friction, heat, and moving parts. | More energy efficient thanks to smooth rotary compression. |
| Noise & Vibration | Higher noise levels and noticeable vibration. | Quiet operation with minimal vibration. |
| Best Suited For | Workshops, automotive bays, small industrial processes. | Large industrial facilities, packaging lines, CNC systems. |
Difference Between Reciprocating and Rotary Screw Air Compressors
Reciprocating and rotary screw air compressors differ in generating and delivering compressed air. Both serve the same purpose. But, each type uses a different compression method. This leads to different performance levels and suitability for various working conditions.
Design, Operation, and Efficiency
Reciprocating compressors and rotary screw systems use different engineering designs. This affects their efficiency, heat management, and how they handle workloads.
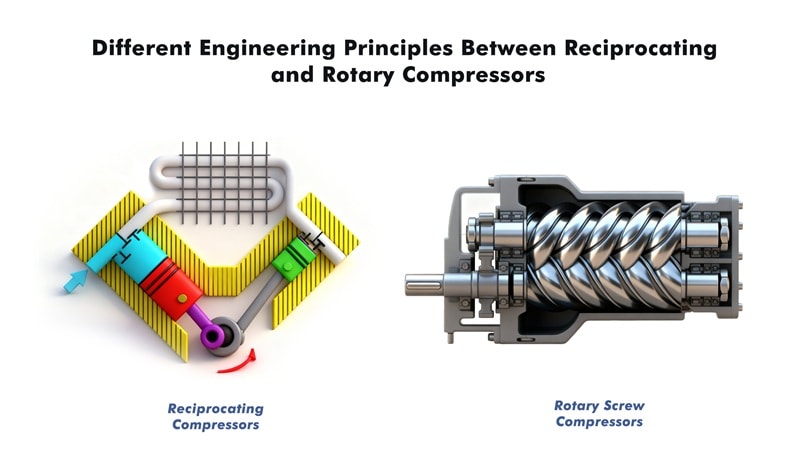
Reciprocating air compressors use pistons driven by a crankshaft inside a cylinder. This design has more moving parts and higher friction. As the pistons move back and forth, they create heat and vibration. They also produce pulsating airflow.
- Different moving parts: pistons, rings, valves, crankshaft.
- Higher heat generation due to friction.
- Strong high pressure air but lower efficiency on long runs.
- More vibration and noise during operation.
- Have a limited duty cycle, making them ideal for intermittent tasks.
Rotary compressors use two meshing helical screws to deliver continuous air compression. They have fewer moving parts and less mechanical impact. As a result, they stay cooler and operate in a more efficient manner.
- Fewer moving parts and minimal internal friction.
- Smooth, stable airflow without pulsation.
- Lower heat generation improves energy efficiency.
- Minimal vibration and quieter operation.
- Built to support 100 duty cycle, meaning they can run in a continuous manner.
Noise Levels, Heat, and Vibration
Rotary screw compressors and reciprocating compressors behave varies in sound, heat, and vibration. These factors affect operator comfort. They also influence equipment wear and system efficiency.
| Feature | Reciprocating Air Compressor | Rotary Screw Air Compressor |
|---|---|---|
| Noise Levels | Higher noise levels due to pistons and crankshaft movement | Lower noise levels with built-in noise reduction features |
| Vibration | Stronger vibration from back-and-forth piston motion | Very low vibration from smooth rotary action |
| Heat Generation | Produces more heat because of constant friction | Generates less heat and stays cooler in long runs |
| Work Environment | Noisy and less stable for enclosed spaces | Quiet and comfortable for industrial facilities |
Maintenance, Durability, and Operating Costs
The long-term efficiency of an air compressor depend on how much maintenance it needs. Reciprocating and rotary screw compressors work in different ways inside the machine. These differences affect service, how long they last, and what they cost to keep running.

Reciprocating air compressor contains several contact-intensive parts that move at high speed. This design requires more maintenance, especially in facilities running frequent start-stop cycles.
- Piston rings, cylinders, and valves face constant friction. They need inspection and replaced on a regular basis.
- The compression chamber generates heat, increasing the wear rate on metal components.
- Regular oil changes are essential. Lubrication breaks down under high pressure and high temperature.
- Continuous piston movement creates vibration. This causes loosen bolts, strain bearings, and reduce efficiency over time.
Reciprocating compressors are reliable for intermittent use or high-pressure tasks. But their maintenance schedule is more demanding. Over time, this contributes to higher operating costs.
Rotary screw air compressor operates on smooth, rotary motion not repetitive mechanical impact. These compressors need less maintenance. But, consistent servicing is still important to protect internal components.
- Air filters: They need regular cleaning or replacement. This prevents dust from entering the rotors and reducing airflow efficiency.
- Oil filters (for oil-lubricated models): They capture contaminants to protect the internal rotors. This helps maintain smooth compression.
- Separator elements: Ensure minimal oil carryover and prevent contamination of downstream equipment.
- Cooling system components: Fans, coolers, and heat exchangers need to keep clean. This controls operating temperature and prevent overheating.
- Drive belts (if belt-driven): It requires periodic tension checks. Replacement is important to maintain proper rotor speed.
- Hoses, seals, and connection points: Inspect for leaks. They can reduce system efficiency and air pressure.
Rotary screw compressors have fewer moving parts. This reduces wear, extends service intervals, and makes maintenance more predictable. Some facilities run for long hours. Others operate in a continuous manner. In these cases, lower maintenance reduces lifetime costs.
Airflow, Pressure Output, and Performance
Both rotary screw and reciprocating compressors are precision-built for completely different performance patterns. So, choosing the right model depends on airflow demand. It also depends on pressure needs and how your facility operates.

Reciprocating compressors deliver high pressure air in short, powerful bursts. Their piston-driven design creates strong compression. But, it delivers a low flow rate. They are best for tools that operate in short bursts. They perform best when pressure output matters more than volume.
Rotary screw compressors provide steady compressed air under heavy load. Their rotor-based design supports long, uninterrupted operation. They are ideal for facilities that need consistent airflow and large air volumes.
Size, Portability, and Installation Requirements

Choosing the right air compressor also depends on available space. It depends on how portable the unit must be and the type of installation required. Reciprocating and rotary compressors differ in size and layout. They also differ in ease of movement and installation.
Reciprocating compressors are generally smaller, lighter, and easier to move. This makes them ideal for environments where portability matters.
- Compact design with a smaller tank, requiring less floor space.
- Easy to transport for mobile tasks or multi-location use.
- Well-suited for workshops, garages, and construction sites.
- A practical choice for a flexible, portable type of air compressor.
Rotary screw compressors deliver long-term placement and high-capacity performance. This results in a bigger and more robust structure.
- Larger footprint, often requiring planned installation.
- Built as heavy duty equipment for continuous industrial use.
- Best suited for permanent setups and integrated compressed air systems.
- Handles high-volume workflows, several tools, and steady gas compression.
- Because of their size and capability, industrial facilities rely on rotary screw models. Equipment stays stationary, and production lines run without interruption.
Choosing the Right Compressor for Your Facility
Understanding how reciprocating and rotary compressors perform inside your facility is important. It helps you choose a system for real operating conditions.

Reciprocating compressors are best for facilities that use short, intermittent cycles. They deliver high-pressure air in powerful bursts. Their pistons, driven by a crankshaft, create more heat and friction. This limits them to a 50–60% duty cycle. Because of this, they are not suitable for continuous operation. They suit single-tool stations with occasional airflow demand.
Best suited when your facility:
- Operates tools in short intervals (2–5 minutes at a time)
- Has natural pauses between tasks that allow cooling
- Uses high-pressure, torque-heavy pneumatic tools
- Needs compressed air as a secondary utility, not a continuous energy source
- Requires strong compression rather than large airflow volume
Runs individual tools such as:
- Impact wrenches
- Punch presses
- Spray guns needing high-pressure bursts
Reciprocating systems also benefit facilities with in-house maintenance teams. As piston rings, valves, and cylinders need periodic servicing. They are ideal for limited infrastructure space like workshops, fabrication bays, maintenance stations.
Rotary screw compressors are useful for facilities that need continuous operation. They provide stable pressure and large, steady airflow. Two meshing helical screws compress the air with minimal friction. This allows a true 100% duty cycle without overheating. They suit high-demand environments with no room for downtime or pressure changes.
Best suited when your facility:
- Runs long production shifts or 24/7 automated operations.
- Requires uninterrupted airflow for CNC machines, robotics, conveyors, or multi-station pneumatic networks.
- Operates several air-powered machines at the same time
- Must avoid pressure drops that could cause defects or downtime.
- Prioritizes energy efficiency and lower cost per CFM.
- Needs a centralized air system with multiple drop points across the plant.
Rotary screw compressors are ideal for facilities with limited maintenance staff. They have fewer moving parts like filters, separators, and cooling systems. They suit permanent industrial installations and compressor rooms. They also work well in large facilities that need steady flow and consistent airflow. Clean, oil-free options support sensitive operations.
Applications of Compressed Air Across Industries
Compressed air is a core utility across industrial facilities. It is often referred to as the “fourth utility” after electricity, gas, and water. Mission-critical equipment relies on compressed air. Modern industries run thousands of pneumatic tools daily.

Manufacturing & Automated Production
Manufacturing environments have some of the highest compressed air demands. The facilities with robotics and continuous automated systems especially have a higher demand.
- Robotic actuators and pick-and-place systems.
- Conveyor controls and packaging machines.
- CNC machines requiring dry, stable air.
- Continuous blow-off, cooling, and drying stations.
- Instrumentation and plant automation systems.
Best compressor type: rotary compressors. They provide steady airflow and an uninterrupted duty cycle. They supply large distribution networks that feed several machines at once. Pressure drops across long piping systems decrease. This ensures consistent performance across the entire facility.
Automotive Workshops, Fabrication Shops & Tool Stations
Small industrial workspaces rely on short bursts of high-pressure air.
- Impact wrenches, ratchets, drills, sanders.
- Tire inflation and suspension systems.
- Spray painting and body shop operations.
- Metal cutting and sheet fabrication tools.
- Bench-top pneumatic equipment.
Best compressor type: reciprocating compressors. They produce high-pressure air in strong bursts. This makes them ideal for on-demand use. They suit shops with fluctuating air needs rather than long, continuous shifts.
Oil & Gas, Petrochemicals, and Heavy Industrial Operations
This sector uses compressed air for tools, but also as an integral part of core process equipment.
- Valve actuation and control systems.
- Pneumatic pumps and blowers.
- Gas compression and vapor recovery.
- Refinery instrumentation systems.
- Offshore platform utility air.
Best compressor type: rotary compressors. They deliver contaminant-free air in harsh conditions. They tolerate high ambient temperatures. They are essential where air system failure is not an option.
Construction, Roadwork & On-Site Industrial Projects
Field operations need portable compressors. These units must power heavy tool loads in unpredictable environments.
- Jackhammers, breakers, rock drills.
- Road paving equipment.
- Sandblasting and surface preparation.
- On-site spray systems and pneumatic cutters.
Best compressor type-Portable reciprocating compressors for high-pressure single-tool use.
Best compressor type: Portable rotary screw units (diesel-driven). They support several tools and deliver large-volume airflow.
The decision depends on whether the site needs one tool or several running at once.
Food, Beverage, Pharmaceutical & High-Purity Industries
Industries such as food, beverage, and pharmaceutical production need clean, oil-free compressed air. This protects sensitive products and meets strict regulatory standards.
- Packaging, bottling, and filling lines.
- Product transport through air conveyors.
- Sterile processing equipment.
- Tablet presses and capsule machines.
- Fermentation control and aeration.
Best compressor type: oil-free rotary compressors. They ensure zero oil carryover in food, drug, and medical processes. These sectors cannot risk contamination, making oil-free systems mandatory rather than optional.
General Industrial Utilities & Facility-Wide Systems
Across broad industrial sectors; electronics, textiles, plastics, warehousing, compressed air powers daily operations.
- Blow molding and injection molding machines.
- Sorting and packaging lines.
- Pneumatic lifts and actuators.
- Central utility air for multiple departments.
- Cleaning, drying, and material handling.
Best compressor type-Rotary screw compressors for continuous flow.
Best compressor type-Reciprocating compressors for isolated, high-pressure workstations.
This depends on whether the facility uses a central system or smaller zones.
FAQs
Which compressor is better for powering several pneumatic tools at once?
A rotary compressor is the better choice. It provides continuous, steady airflow without pressure drops. Reciprocating units can power more than one tool. But, their low flow rate limits sustained multi-tool operation.
How does duty cycle affect compressor performance?
Duty cycle shows how long a compressor can run. Reciprocating compressors support intermittent use. Rotary screw models can operate at a 100% duty cycle. This makes them ideal for long, uninterrupted industrial shifts.
Are rotary screw compressors suitable for harsh temperatures?
Yes. Their design generates less heat, and with fewer moving parts. They perform without interruption in both hot and cold industrial environments. Reciprocating units may overheat under continuous use in extreme conditions.
Do only food and pharma industries need oil-free compressors?
No. Any industry that cannot risk oil carryover benefits from oil-free rotary screw compressors. This includes electronics, medical devices, and laboratories.
What common mistake do facilities make when selecting a compressor?
Many choose based on pressure alone. Total airflow demand is often ignored. This leads to selecting a high-pressure reciprocating unit. Often, the facility actually needs continuous compressed air. A rotary screw compressor is the better choice.
Airflow demand determines the choice between reciprocating and rotary screw compressors. It also depends on your facility’s duty cycle. You also need to consider pressure needs and how much maintenance your team can handle. Reciprocating units deliver powerful high pressure air for short, intermittent tasks. The rotary compressors provide the steady flow and efficiency for continuous industrial operation. Match the compressor type to your industrial application and equipment load. Consider long-term performance goals. This ensures a reliable, cost-effective, and future-ready compressed air system.
Experience the next level of compressed air performance with GiantAir. Our engineered solutions deliver stable airflow and high efficiency. They also provide long-term reliability for demanding industrial facilities. Connect with our team today. Request the product catalog to choose a compressor system for your operational needs.



